Översägt vs. Översatt: Understanding Common Translation Errors in Swedish
Language learners and translation software often stumble when faced with similar-looking words. In Swedish, two…
Lost in Transliteration: Why ‘gthtdjxbr’ Actually Means ‘Translator’
If you've ever encountered the term “gthtdjxbr” online and wondered what it means, you're not…
The Linguistic Impact of Typos: Decoding ‘çevş’ in Online Turkish Conversations
Misspelled words often reveal more about language than their correct counterparts. One such term is…
How Gibberish Like ‘jvhksgdj’ Ends Up Trending Online
In the digital age, even strings of meaningless characters like "jvhksgdj" can gain unexpected popularity.…
Was Carnaval De Oruro Bolivia 1884 Cancelado? A Historical Investigation
The Carnaval de Oruro, one of Bolivia’s most important cultural celebrations, has a rich history…
From ‘переводчитк’ to ‘переводчик’: Common Russian Typos in Online Translation
Misspellings in non-Latin alphabets can be especially problematic, and the Russian typo “переводчитк” is a…
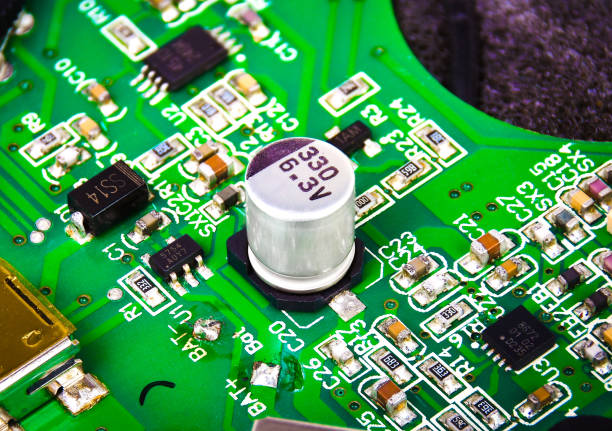
Maximizing Efficiency in Compact Circuit Designs with 20V 1000uF SMD 4 x 5.4mm Electrolytic Capacitor SnapMagic
In today’s age of miniaturized electronics, engineers and circuit designers are constantly searching for components…
rvsn_inkforyourself_customjournal_1_0_1: A Deep Dive Into the Self-Discovery Journal Everyone’s Talking About
In an era of digital chaos and ever-increasing demands on our attention, one tool has…
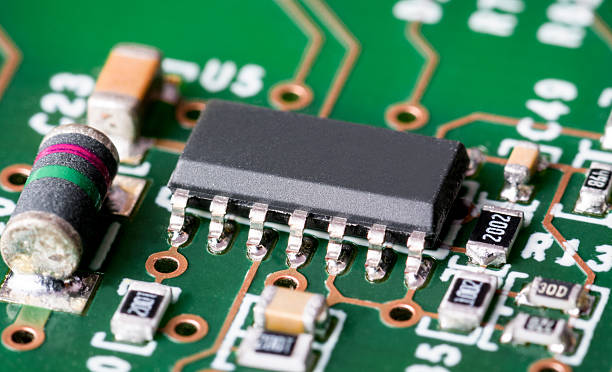
Top Mistakes to Avoid When Placing 20V 1000uF SMD 4 x 5.4mm Electrolytic Capacitor KiCad PCB Layouts
When working on compact and efficient PCB designs, electrolytic capacitors play a critical role in…
Designing with Precision: Integrating 25v 1000uf SMD 4 x 5.4mm Electrolytic Capacitor KiCad for Compact PCB Layouts
In the evolving world of electronics design, every millimeter of space on a printed circuit…